Abstract
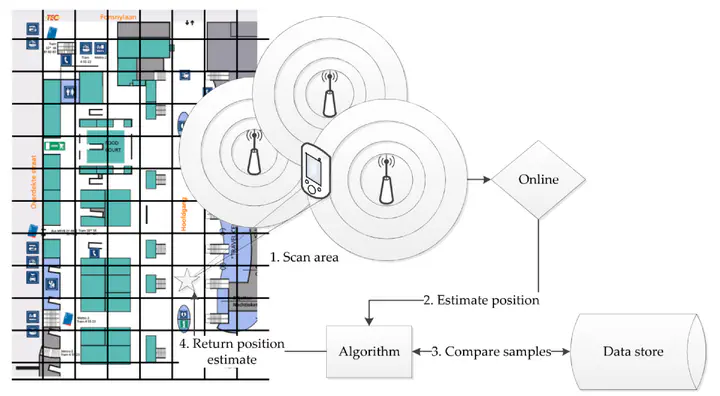
Recently, the domain of navigational applications has seen a huge rise. Due to the rising popularity of smartphones which are nowadays equipped with Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers, a great number of people who own these devices have the possibility to easily get information about their position and have a greater need for good navigational applications. Such applications, for example Google maps, work great when used outdoors. However, when we try to use these applications indoors, we have major problems in finding our correct position. Because the GPS needs to have an unobstructed line of sight to the GPS satellites, we encounter problems when trying to locate our position indoors. Some theoretical aspects have to be covered, concerning radiolocation and indoor positioning, before we can continue by summarising the various different solutions that already exists in other projects, each with their own use of specific technologies and techniques. We will see that most of these were created for specific hardware and using some explicit algorithm however. And despite the fact that there exist a number of frameworks, they all have their own limitations. Therefore, in this thesis we explore the notion of an Indoor Positioning System (IPS) in terms of a framework that works for various mobile devices and is extensible to be used with numerous algorithms and techniques. The design and implementation of this framework is discussed in detail and afterwards, an example IPS that uses Wireless local area network (WLAN) infrastructure and works with the Android platform is implemented using the framework. Several test were performed on the performance of this system, which are also presented.